Why Mining Matters
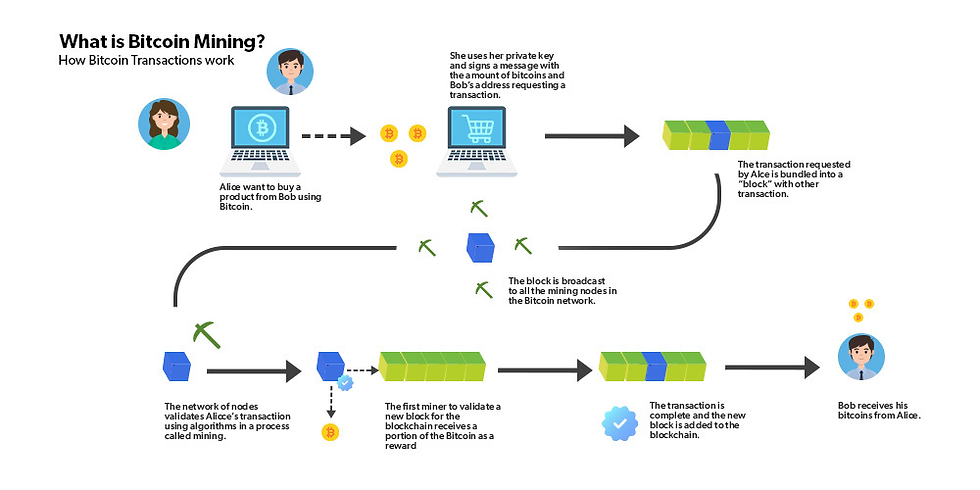
Bitcoin mining is the process by which new bitcoins are created and transactions are verified on the Bitcoin network. Miners use specialized computer hardware to solve complex mathematical problems, securing the network and earning rewards in the form of newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees.
Network Security
Mining prevents double-spending by ensuring all transactions are immutable once added to the blockchain. The computational effort required makes it nearly impossible for malicious actors to alter the ledger without controlling 51% of the network’s computing power.
Decentralization
It enables a trustless system where no central authority controls the network, aligning with Bitcoin’s ethos of financial sovereignty.
New Bitcoin Creation
Mining introduces new Bitcoins into circulation, with the reward halving every four years (next halving in 2028) until the 21 million cap is reached around 2140.
Bitcoin Mining at a Glance
Key Terms
Core Bitcoin Terms
Crypto currency: A digital or virtual form of money that uses cryptography for security and operates on a decentralized network, typically a blockchain. Unlike traditional currencies issued by governments (fiat money), cryptocurrencies are not controlled by any central authority, such as a central bank.
Bitcoin: A digital currency that operates on a decentralized peer-to-peer network. It allows for secure and transparent transactions without needing intermediaries like banks.
Bitcoin Mining: The process of validating and adding new transactions to the Bitcoin blockchain by solving complex mathematical problems. Miners are rewarded with newly created Bitcoin, known as the "block reward".
Proof Of Work (PoW): The consensus mechanism used by Bitcoin, where miners compete to solve a complex mathematical problem. The first miner to solve the problem gets to add a new block to the blockchain and receive the block reward.
Block: A group of transactions that are confirmed and added to the blockchain. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data.
Block Reward: The amount of Bitcoin earned by the miner who completes the mathematical calculation (hashing) and adds a new block of transactions to the blockchain. This occurs approximately every 10 minutes and is paid out daily at 6 p.m. PT and converted to cash.
Blockchain: A digital ledger technology that securely records transactions across a distributed network of computers.
Operations
Halving: An event that occurs approximately every four years, where the block reward for mining a new block is cut in half. This is designed to control the supply of Bitcoin.
Difficulty:A measure of how hard it is to mine a new block in the Bitcoin network. The difficulty adjusts approximately every two weeks based on the total computing power of the network.
Mining Pool: A group of miners combine their computational power (hash rate) to increase their chances of earning block rewards. The rewards are shared among the pool members based on the amount of hash rate they contribute.
Hashing: The process of converting information into a fixed-length code using a mathematical function. In Bitcoin mining, hashing is used to solve complex problems that validate transactions.
Hash Rate: The speed at which a miner can compute hashes. A higher hash rate increases the chances of earning bitcoin rewards.
Hashprice: Hash Price (or "hashprice") is the market value assigned per unit of hashing power. Hashprice is measured by dollars per terahash per second per day ($/TH/s/d). The term coined by Luxor in 2019 - quantifies how much a digital miner can expect to earn from a specific quantity of hashrate. It is influenced by factors like cryptocurrency price, the difficulty factor, and transaction fees.
Uptime: The percentage of time your mining equipment is actively operating and generating hash power.
Electricity Rate: the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electrical power consumed by mining operations.
Hardware
ASIC (Application-Specific Integrated Circuit): Specialized hardware designed for mining Bitcoin. ASICs are much more efficient at mining than general purpose CPUs or GPUs.
Miner: A machine (usually an ASIC)or group of machines that performs complex mathematical calculations (hashing) to solve cryptographic puzzles and validate blocks of transactions to win the bitcoin reward.
Immersion Cooling Technology: A method of cooling mining equipment by immersing it in a non-conductive liquid. This reduces heat and energy consumption, improving efficiency and lowering costs.
Bitcoin Mining Container: A modular, pre-fabricated, and mobile data center designed specifically to house and operate Bitcoin mining equipment—primarily ASIC miners—in a compact and efficient environment.
Dielectric Fluid: a specialized liquid coolant that does not conduct electricity, used in advanced Bitcoin mining cooling systems for direct contact with electronic components.
Cooling System: Infrastructure designed to remove excess heat generated by mining equipment (ASICs). Mining rigs consume massive amounts of electricity and generate significant heat as a byproduct of the computational work required to solve cryptographic puzzles.
Hash board: (also called a mining board) is the core computational component of an ASIC miner that contains the specialized chips responsible for performing Bitcoin's SHA-256 hashing algorithm.
Valiant Funds
867 Boylston Street, 5th Floor, Suite 1581 Boston, MA 02116
877-690-8983
© 2025 Valiant Finance
Important Investor Information
Alternative investments involve substantial risk and are suitable only for sophisticated investors who can afford to lose their entire investment. These investments are illiquid, typically requiring long-term commitments with limited ability to withdraw funds before maturity. Alternative investments are not insured by the FDIC or any other government agency, and there is no guarantee of returns or preservation of capital. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Prospective investors should carefully review all offering materials and consult with qualified financial, tax, and legal advisors before making any investment decision.
